在现代Java开发中,对象之间的属性拷贝是一个常见的需求。Spring框架提供的org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties方法因其简洁性和易用性而被广泛使用。然而,尽管该方法在大多数情况下能够满足需求,但在实际应用中仍存在一些潜在的问题和陷阱。本文将详细介绍使用copyProperties时常见的11个问题,并提供相应的解决方案和替代方案,帮助开发者更好地理解和使用这一工具。
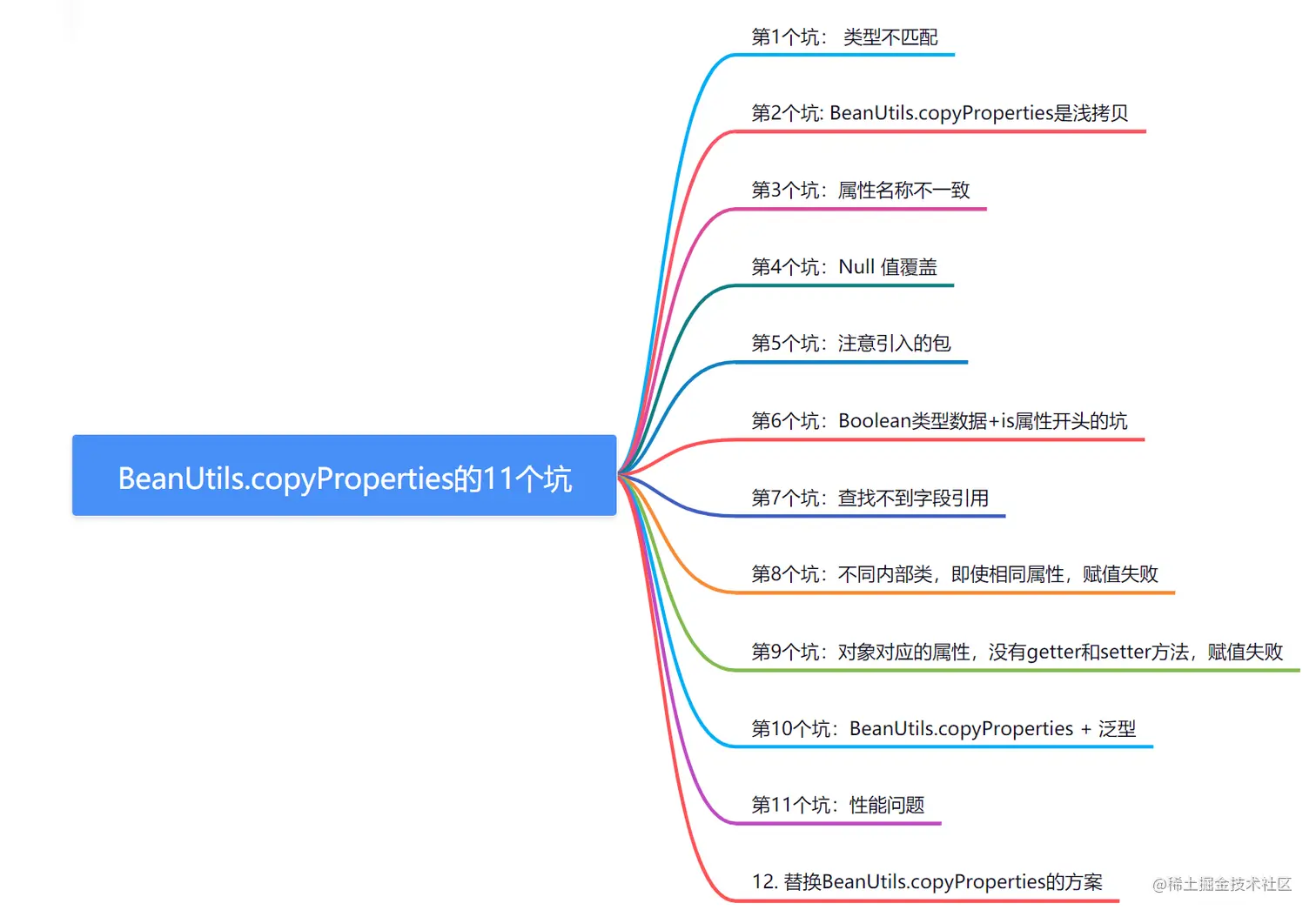
第1个坑: 类型不匹配
@Data
public class SourceBean {
private Long age;
}
@Data
public class TargetBean {
private String age;
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SourceBean source = new SourceBean();
source.setAge(25L);
TargetBean target = new TargetBean();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target);
System.out.println(target.getAge()); //拷贝赋值失败,输出null
}
}
在上述demo中,源对象SourceBean的age属性是一个Long类型,而目标对象TargetBean的age属性是一个String类型。由于类型不匹配,BeanUtils.copyProperties不会赋值成功的。我跑demo的结果,控制台输出null。
第2个坑: BeanUtils.copyProperties是浅拷贝
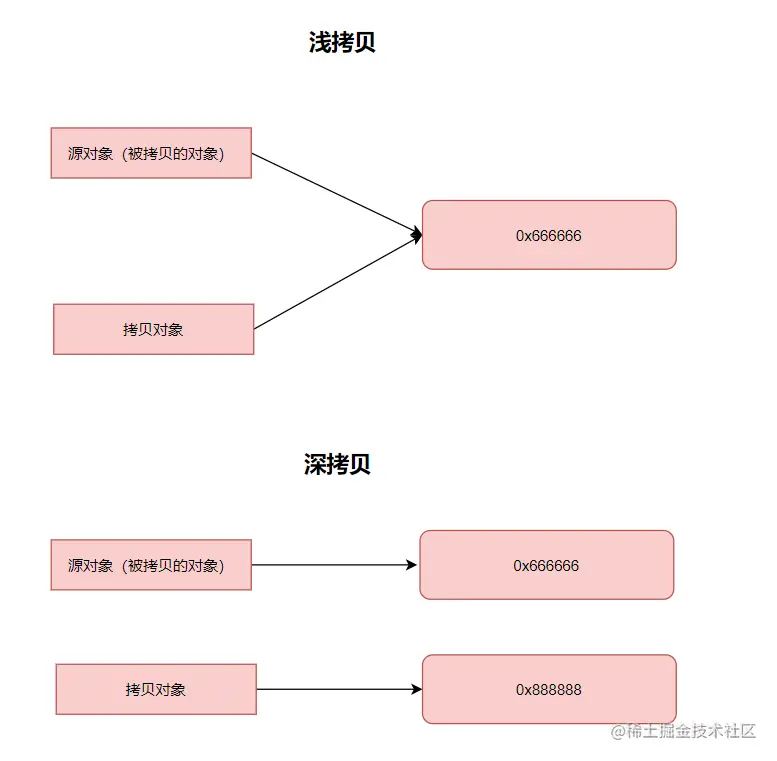
先给大家复习一下,什么是深拷贝?什么是浅拷贝?
浅拷贝是指创建一个新对象,该对象的属性值与原始对象相同,但对于引用类型的属性,仍然共享相同的引用。换句话说,浅拷贝只复制对象及其引用,而不复制引用指向的对象本身。
深拷贝是指创建一个新对象,该对象的属性值与原始对象相同,包括引用类型的属性。深拷贝会递归复制引用对象,创建全新的对象,以确保拷贝后的对象与原始对象完全独立。
我再给个代码demo给大家看看哈:
public class Address {
private String city;
//getter 和 setter 方法省略
}
public class Person {
private String name;
private Address address;
//getter 和 setter 方法省略
}
Person sourcePerson = new Person();
sourcePerson.setName("John");
Address address = new Address();
address.setCity("New York");
sourcePerson.setAddress(address);
Person targetPerson = new Person();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourcePerson, targetPerson);
sourcePerson.getAddress().setCity("London");
System.out.println(targetPerson.getAddress().getCity()); // 输出为 "London"
在上述示例中,源对象Person的属性address是一个引用类型。当使用BeanUtils.copyProperties方法进行属性复制时,实际上只复制了引用,即目标对象targetPerson的 address 属性引用和源对象 sourcePerson 的 address 属性引用指向同一个对象。因此,当修改源对象的address对象时,目标对象的address对象也会被修改。
大家日常开发中,要注意这个坑哈~
第3个坑:属性名称不一致
public class SourceBean {
private String username;
// getter 和 setter 方法省略
}
public class TargetBean {
private String userName;
// getter 和 setter 方法省略
}
SourceBean source = new SourceBean();
source.setUsername("捡田螺的小男孩");
TargetBean target = new TargetBean();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target);
System.out.println(target.getUserName()); // 输出为 null
在上述示例中,源对象SourceBean 的属性名称是username,而目标对象TargetBean的属性名称也是userName。但是,两个 username,一个N是大写,一个n是小写,即属性名称不一致,BeanUtils.copyProperties方法无法自动映射这些属性(无法忽略大小写自动匹配),因此目标对象的userName属性值为null。
大家日常开发中,要注意这个坑哈~ 比如大小写不一致,差一两个字母等等。
第4个坑:Null 值覆盖
@Data
public class SourceBean {
private String name;
private String address;
}
@Data
public class TargetBean {
private String name;
private String address;
}
SourceBean source = new SourceBean();
source.setName("John");
source.setAddress(null);
TargetBean target = new TargetBean();
target.setAddress("田螺address");
BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target);
System.out.println(target.getAddress()); // 输出为 null在上述示例中,源对象 SourceBean 的 address 属性值为 null。默认情况下,BeanUtils.copyProperties 方法会将源对象中的 null 值属性覆盖到目标对象中。因此,目标对象的 address 属性值也为 null。
如果你不希望 null 值覆盖目标对象中的属性,可以使用 BeanUtils.copyProperties 方法的重载方法,并传入一个自定义的 ConvertUtilsBean 实例来进行配置。
第5个坑:注意引入的包
BeanUtils.copyProperties其实有两个包,分别是spring、apache。大家注意一下哈,这两个包,是有点不一样的:
//org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils(源对象在左边,目标对象在右边) public static void copyProperties(Object source, Object target) throws BeansException //org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils(源对象在右边,目标对象在左边) public static void copyProperties(Object dest, Object orig) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException
大家使用的时候,要注意一下哈,千万注意自己引入的哪个BeanUtils,写对应参数位置。
第6个坑:Boolean类型数据+is属性开头的坑
把SourceBean和TargetBean中的都有个属性isTianLuo,它们的数据类型保持不变,但是一个为基本类型boolean,一个为包装类型Boolean
@Data
public class SourceBean {
private boolean isTianLuo;
}
@Data
public class TargetBean {
private Boolean isTianLuo;
}跑测试用里的时候,发现赋值不上:
SourceBean source = new SourceBean(); source.setTianLuo(true); TargetBean target = new TargetBean(); BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target); System.out.println(target.getIsTianLuo()); // 输出为 null
为什么呢?即使是一个包装类型,一个基本类型,应该可以赋值上才对的。
这是因为当属性类型为
boolean时,属性名以is开头,属性名会去掉前面的is,因此源对象和目标对象属性对不上啦。
大家使用BeanUtils.copyProperties过程中,要注意哈~
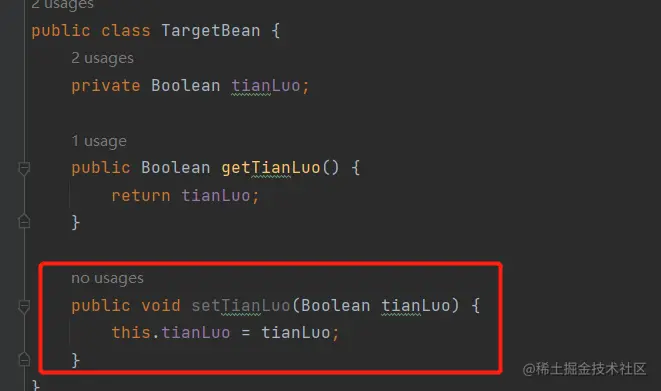
第7个坑:查找不到字段引用
在某些开发场景呢,如果我们要修改某个字段的赋值,我们可能会全文搜索它的所有set方法,看哪些地方引用到。
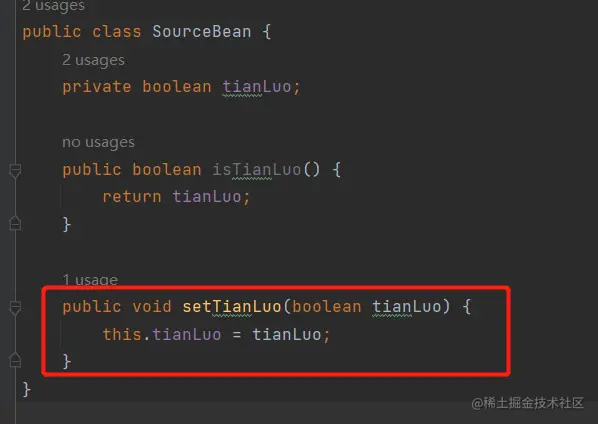
但是呢,如果使用BeanUtils.copyProperties,就不知道是否引用到对应的ste方法啦,即查找不到字段引用。这就可能导致你会漏掉修改对应的字段。
第8个坑:不同内部类,即使相同属性,也是赋值失败
@Data
public class CopySource {
public String outerName;
public CopySource.InnerClass innerClass;
@Data
public static class InnerClass {
public String InnerName;
}
}
@Data
public class CopyTarget {
public String outerName;
public CopyTarget.InnerClass innerClass;
@Data
public static class InnerClass {
public String InnerName;
}
}
CopySource test1 = new CopySource();
test1.outerName = "outTianluo";
CopySource.InnerClass innerClass = new CopySource.InnerClass();
innerClass.InnerName = "innerTianLuo";
test1.innerClass = innerClass;
System.out.println(test1);
CopyTarget test2 = new CopyTarget();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(test1, test2);
System.out.println(test2); //输出CopyTarget(outerName=outTianluo, innerClass=null)
以上demo中,CopySource和CopyTarget各自存在一个内部类InnerClass,虽然这个内部类属性也相同,类名也相同,但是在不同的类中,因此Spring会认为属性不同,不会Copy;
如果要复制成功,可以让他们指向同一个内部类。
第9个坑:bean对应的属性,没有getter和setter方法,赋值失败
BeanUtils.copyProperties要拷贝属性值成功,需要对应的bean要有getter和setter方法。因为它是用反射拿到set和get方法再去拿属性值和设置属性值的。
@Data
public class SourceBean {
private String value;
}
@Getter //没有对应的setter方法
public class TargetBean {
private String value;
}
SourceBean source = new SourceBean();
source.setValue("捡田螺的小男孩");
TargetBean target = new TargetBean();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target);
System.out.println(target.getValue()); //输出null第10个坑:BeanUtils.copyProperties + 泛型
如果BeanUtils.copyProperties遇到泛型,也是很可能赋值失败的哈。大家看下这个例子:
@Data
public class CopySource {
public String outerName;
public List<CopySource.InnerClass> clazz;
@Data
public static class InnerClass {
public String InnerName;
}
}
@ToString
@Data
public class CopyTarget {
public String outerName;
public List<CopyTarget.InnerClass> clazz;
@Data
public static class InnerClass {
public String InnerName;
}
}
CopySource test1 = new CopySource();
test1.outerName = "outTianluo";
CopySource.InnerClass innerClass = new CopySource.InnerClass();
innerClass.InnerName = "innerTianLuo";
List<CopySource.InnerClass> clazz = new ArrayList<>();
clazz.add(innerClass);
test1.setClazz(clazz);
System.out.println(test1);
CopyTarget test2 = new CopyTarget();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(test1, test2);
System.out.println(test2); //输出CopyTarget(outerName=outTianluo, clazz=null)
这里面的例子,BeanUtils.copyProperties方法拷贝包含泛型属性的对象clazz。CopyTarget和CopySource的泛型属性类型不匹配,因此拷贝赋值失败。
如果是低版本的包,泛型如果不匹配,则会报错,高本版则知识拷贝赋值失败。
第11个坑:性能问题
由于这些BeanUtils类都是采用反射机制实现的,对程序的效率也会有影响。我跑了个demo对比:
SourceBean sourceBean = new SourceBean();
sourceBean.setName("tianLuoBoy");
TargetBean target = new TargetBean();
long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { //循环10万次
target.setName(sourceBean.getName());
}
System.out.println("common setter time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime));
long beginTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { //循环10万次
BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourceBean, target);
}
System.out.println("bean copy time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime1));
//输出
common setter time:3
bean copy time:331
可以发现,简单的setter和BeanUtils.copyProperties对比,性能差距非常大。因此,慎用BeanUtils.copyProperties!!!
12. 替换BeanUtils.copyProperties的方案
以上聊了BeanUtils.copyProperties的11个坑,都是在跟大家聊,要慎用BeanUtils.copyProperties。那有没有推荐替换它的方案呢。
第一种,那就是使用原始的setter和getter方法。
使用手动的setter方法进行属性赋值。这种方法可能需要编写更多的代码,但是可以提供更细粒度的控制,并且在性能方面通常比BeanUtils.copyProperties更高效。
Target target = new Target(); target.setName(source.getName()); target.setAge(source.getAge());
如果实在对象bean的属性比较多的话,可以使用插件GenerateAllSetter,它可以一键生成对象的set方法,挺方便的。
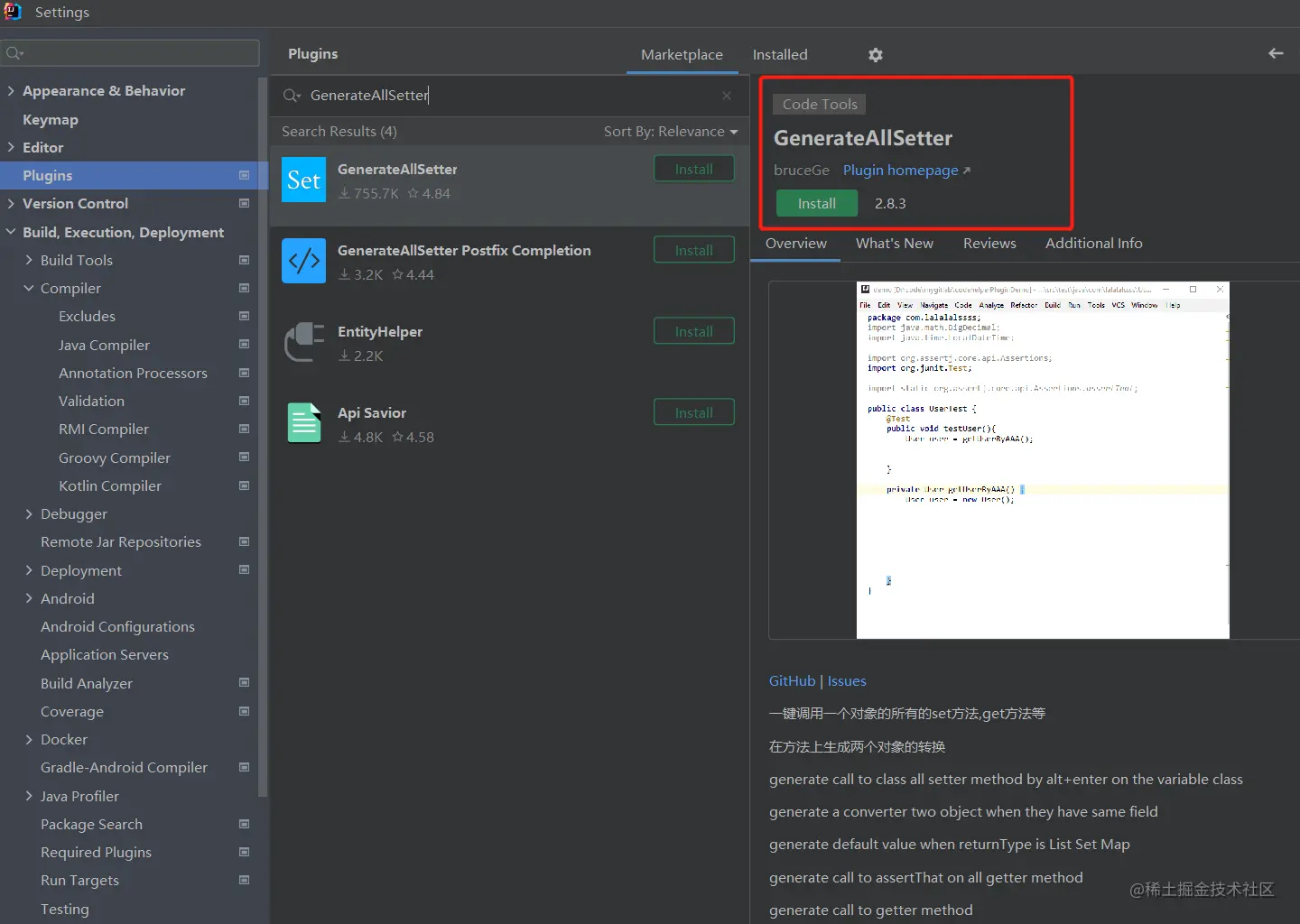
第二种方案,使用映射工具库,如MapStruct、ModelMapper等,它们可以自动生成属性映射的代码。这些工具库可以减少手动编写setter方法的工作量,并提供更好的性能。
使用MapStruct的示例:
@Mapper
public interface SourceTargetMapper {
SourceTargetMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(SourceTargetMapper.class);
@Mapping(source = "name", target = "name")
@Mapping(source = "age", target = "age")
Target mapToTarget(Source source);
}
Target target = SourceTargetMapper.INSTANCE.mapToTarget(source);总结
通过本文的介绍,我们总结了使用org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties方法时可能遇到的11个常见问题,包括类型不匹配、浅拷贝、属性名称不一致、Null值覆盖、包引入错误、Boolean类型数据问题、查找不到字段引用、不同内部类赋值失败、缺少getter和setter方法、泛型属性赋值失败以及性能问题。针对这些问题,本文提供了详细的解释和示例,并推荐了两种替代方案:手动使用setter和getter方法以及使用映射工具库如MapStruct和ModelMapper。希望本文能帮助开发者在实际项目中更加高效和安全地进行对象属性拷贝操作。
本文来源于#捡田螺的小男孩,由@蜜芽 整理发布。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系本站客服处理!
该文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:https://www.zhanid.com/biancheng/2493.html