在Web开发中,精准控制元素的位置是实现美观布局的关键。JavaScript中的offsetLeft和offsetTop属性便是开发者手中的有力工具,它们允许动态获取和设置元素相对于其包含块的水平和垂直偏移量。本文将深入探讨这两个属性的使用方法,帮助开发者更好地理解和应用它们,从而提升Web页面的交互性和用户体验。

一、第一个小例子
<body>
<style>
body { margin:0; }
.box1 { width:300px; height:300px; margin:100px; background:#333; overflow:hidden; }
.box2 { width:200px; height:200px; margin:100px; background:#666; overflow:hidden; }
.box3 { width:100px; height:100px; margin:100px; background:#999;}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var oBox1 = document.querySelector('.box1');
var oBox2 = document.querySelector('.box2');
var oBox3 = document.querySelector('.box3');
console.log('box1: '+ oBox1.offsetLeft +','+ oBox1.offsetTop);
console.log('box2: '+ oBox2.offsetLeft +','+ oBox2.offsetTop);
console.log('box3: '+ oBox3.offsetLeft +','+ oBox3.offsetTop);
</script>
</body>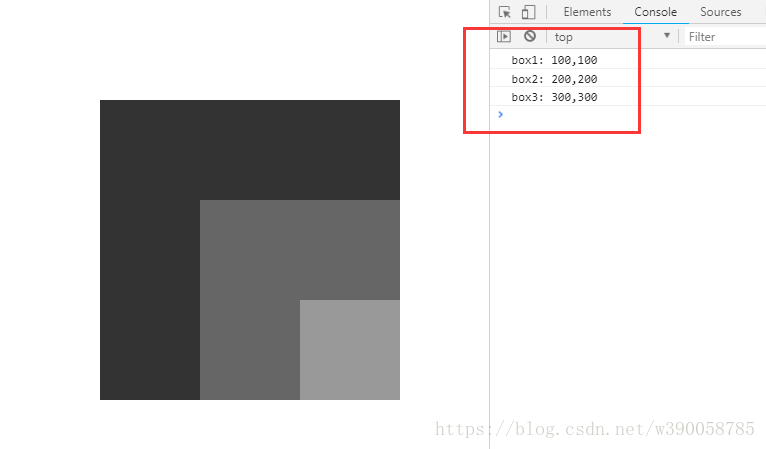
①第一个例子中,三个div的上一级的定位元素都是body,body是最外层的定位元素,三个div获取到的offsetLeft值跟offsetTop值都是相对于body的偏移量。
二、第二个小例子(给box1添加相对定位)
<body>
<style>
body { margin:0; }
.box1 { width:300px; height:300px; margin:100px; background:#333; overflow:hidden; position:relative;}
.box2 { width:200px; height:200px; margin:100px; background:#666; overflow:hidden; }
.box3 { width:100px; height:100px; margin:100px; background:#999;}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var oBox1 = document.querySelector('.box1');
var oBox2 = document.querySelector('.box2');
var oBox3 = document.querySelector('.box3');
console.log('box1: '+ oBox1.offsetLeft +','+ oBox1.offsetTop);
console.log('box2: '+ oBox2.offsetLeft +','+ oBox2.offsetTop);
console.log('box3: '+ oBox3.offsetLeft +','+ oBox3.offsetTop);
</script>
</body>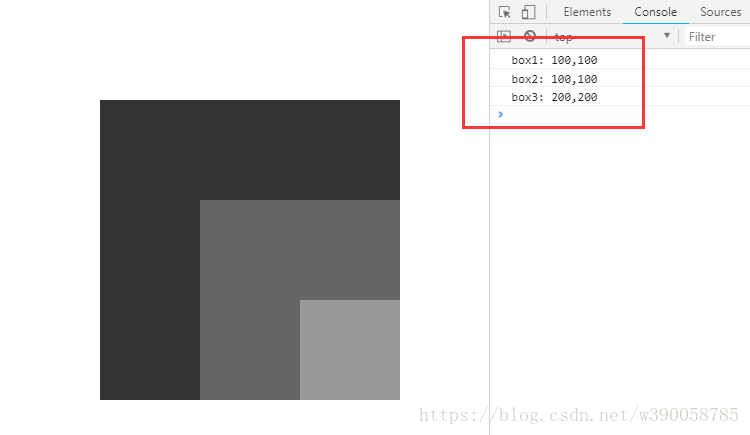
②第二个例子中,box1加上了相对定位,这时候box2,box3的上一级定位元素不再是body了,这时他们获取到的offsetLeft值跟offsetTop值都是相对于box1的偏移量。而box1的上一级定位元素还是body,所以他的偏移量还是相对于body的。
三、第三个小例子(给box1,box2添加相对定位)
<body>
<style>
body { margin:0; }
.box1 { width:300px; height:300px; margin:100px; background:#333; overflow:hidden; position:relative; }
.box2 { width:200px; height:200px; margin:100px; background:#666; overflow:hidden; position:relative; }
.box3 { width:100px; height:100px; margin:100px; background:#999;}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var oBox1 = document.querySelector('.box1');
var oBox2 = document.querySelector('.box2');
var oBox3 = document.querySelector('.box3');
console.log('box1: '+ oBox1.offsetLeft +','+ oBox1.offsetTop);
console.log('box2: '+ oBox2.offsetLeft +','+ oBox2.offsetTop);
console.log('box3: '+ oBox3.offsetLeft +','+ oBox3.offsetTop);
</script>
</body>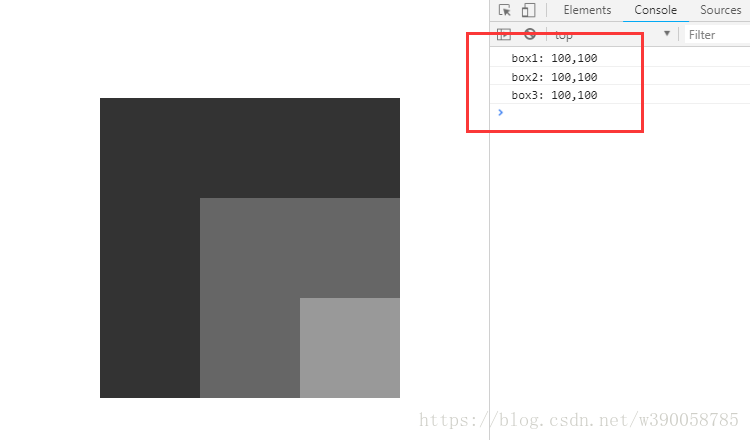
③第三个例子中,box1跟box2都加上了相对定位,这时候,box3的上一级定位元素变成是box2,box2的上一级定位元素是box1,box1的上一级定位元素还是body。所以这时候就出现了。三个div的偏移量都为100;
四、解析
通过上面的三个例子不难看出,offsetLeft值跟offsetTop值的获取跟父级元素没关系,而是跟其上一级的定位元素(除position:static;外的所有定位如fixed,relative,absolute)有关系。
五、扩展(在第三个例子中,假如我想获取到box3到浏览器窗口的偏移量,该怎么去获取呢?)
思路很简单,就是把元素本身的偏移量跟所有上级定位元素的偏移量都加起来就可以了,问题又来了,假如我们不知道他有几个上级定位元素呢?
其实也不难。js不但提供了offsetLeft、offsetTop方法,还提供了offsetParent(获取上一级定位元素对象)的方法。所以现在我们只需封装一个函数就可以了。
function offset(obj,direction){
//将top,left首字母大写,并拼接成offsetTop,offsetLeft
var offsetDir = 'offset'+ direction[0].toUpperCase()+direction.substring(1);
var realNum = obj[offsetDir];
var positionParent = obj.offsetParent; //获取上一级定位元素对象
while(positionParent != null){
realNum += positionParent[offsetDir];
positionParent = positionParent.offsetParent;
}
return realNum;
}运用程序中
<body>
<style>
body { margin:0; }
.box1 { width:300px; height:300px; margin:100px; background:#333; overflow:hidden; position:relative; }
.box2 { width:200px; height:200px; margin:100px; background:#666; overflow:hidden; position:relative; }
.box3 { width:100px; height:100px; margin:100px; background:#999;}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var oBox1 = document.querySelector('.box1');
var oBox2 = document.querySelector('.box2');
var oBox3 = document.querySelector('.box3');
function offset(obj,direction){
//将top,left首字母大写,并拼接成offsetTop,offsetLeft
var offsetDir = 'offset'+ direction[0].toUpperCase()+direction.substring(1);
var realNum = obj[offsetDir];
var positionParent = obj.offsetParent; //获取上一级定位元素对象
while(positionParent != null){
realNum += positionParent[offsetDir];
positionParent = positionParent.offsetParent;
}
return realNum;
}
console.log('box1: '+ offset(oBox1,'left') +','+ offset(oBox1,'top'));
console.log('box2: '+ offset(oBox2,'left') +','+ offset(oBox2,'top'));
console.log('box3: '+ offset(oBox3,'left') +','+ offset(oBox3,'top'));
</script>
</body>运行结果为:
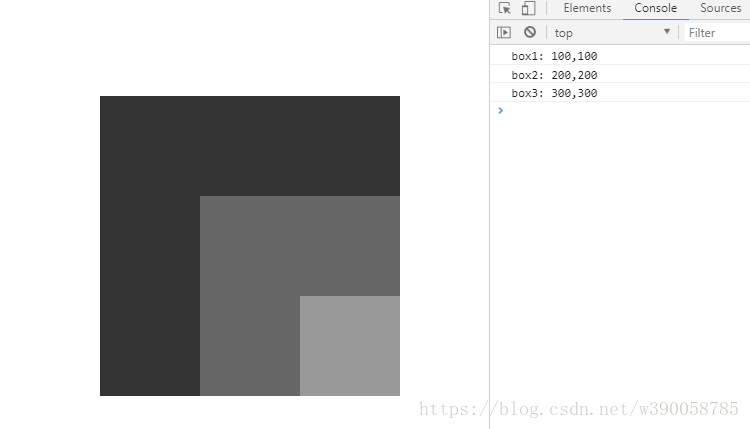
总结:
通过本文的详细解析,我们了解到offsetLeft和offsetTop不仅是获取元素位置的强大工具,还可以用于动态调整元素的位置,实现丰富的视觉效果。掌握这些技巧,可以让我们的Web开发工作更加得心应手,同时也为创建更加互动和响应式的网页奠定了坚实的基础。记住,合理利用这些属性,可以大大增强用户体验,但也要注意避免过度使用,以免影响页面性能。
本文来源于#汪小穆,由@ZhanShen 整理发布。如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系本站客服处理!
该文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:https://www.zhanid.com/biancheng/1915.html